Government of Gujarat Endorses GPCB’s Powerful Circular on Revised Industrial Siting Criteria
Siting Criteria for Industrial Projects in Gujarat (GPCB Guidelines)
Establishing a new industrial unit or expanding an existing one in Gujarat requires strict adherence to environmental norms laid down by the Gujarat Pollution Control Board (GPCB). Site selection plays a pivotal role in minimizing environmental degradation and ensuring sustainable industrial growth. Over the years, GPCB has issued multiple guidelines and circulars to govern the siting process for industries across the state.
Background of GPCB Siting Criteria
In 1998, the Government of Gujarat and the GPCB issued a circular (બખ૫/૧૦૯૮/યુ.ઓ.૧૨/ક, dated 30/10/1998) stating that obtaining GPCB’s approval was not mandatory for converting agricultural land into non-agricultural (industrial) use. This circular essentially simplified the process of land conversion for industrial purposes at the time.
However, with increasing concerns over environmental protection and the need for planned industrial development, the GPCB revised its stance. A subsequent circular (Circular No. ગુ. પ્ર. નિ બોર્ડ / પરિપત્ર / એન.જે / 1 / 06 / 10253, dated 12/04/2006) introduced more stringent guidelines for granting non-agricultural permissions. These updated norms required land conversion for industrial use to fulfil specific environmental and locational criteria.
Key Factors in Industrial Site Selection
The revised GPCB guidelines consider several critical parameters for approving industrial sites:
-
Distance from Residential Areas: To safeguard public health and quality of life, industries—especially those with higher pollution potential—must be located at a safe distance from residential colonies, schools, and hospitals.
-
Proximity to Water Bodies: Industries must not be located near lakes, rivers, canals, or other natural water bodies to avoid water contamination. Buffer zones are often mandated around such ecological features.
-
Ecologically Sensitive Zones: No industrial activity is permitted in protected areas such as wildlife sanctuaries, national parks, and eco-sensitive zones without strict scrutiny and clearances.
-
Groundwater Availability and Vulnerability: Industries requiring large amounts of water or discharging effluents must consider the impact on local groundwater quality and quantity.
-
Infrastructure Availability: Road access, power supply, waste management facilities, and connectivity are also considered in evaluating industrial site suitability.
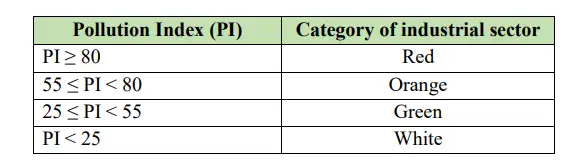
Pollution Index (PI) and Industrial Categorization
To streamline the approval process and align environmental impact assessments with pollution potential, the GPCB adopted the Pollution Index (PI) system developed by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
Industries are categorized into four groups based on their PI scores:
-
Red Category: These industries have a high pollution potential. Examples include chemical manufacturing, thermal power plants, and tanneries. They face the strictest regulations and cannot be set up in ecologically sensitive or densely populated areas.
-
Orange Category: Medium pollution potential industries such as textile processing or food processing fall under this category. These projects still require environmental clearance and site scrutiny.
-
Green Category: Low pollution potential industries like assembly units and small-scale engineering operations. These have relatively relaxed site selection criteria.
-
White Category: Non-polluting industries such as software development or educational institutions. These are often exempt from prior environmental clearance but must still meet basic siting norms.
Importance of Environmental Clearance
For any industrial project to commence, it is mandatory to secure the necessary environmental consents and clearances from GPCB. This includes:
-
Consent to Establish (CTE) under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 and the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
-
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) for Red and some Orange category projects.
-
Adherence to Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) norms where applicable.
-
Hazardous Waste Management compliance for industries handling toxic substances.
Conclusion
The siting of industrial projects in Gujarat is no longer just a matter of land availability or proximity to markets. With the GPCB’s evolving framework, environmental sustainability has become a central criterion. Businesses planning to set up or expand industrial operations must strictly follow the GPCB siting criteria, ensuring minimal environmental impact and smooth regulatory approvals.
| Sr. No. | Location | Distance (Meter) | ||
| As per Industrial Unit (by C.P.C.B. Category) | ||||
| Red | Orange | Green | ||
| 01 | Residential/School/Collage | 500 | 250 | 200 |
| 02 | River/Pond/Natural drain/ lake | 500 | 250 | 150 |
| 03 | Regarding the distance of the industrial unit from roads, railways, canals, and historical buildings, the minimum distance must be maintained as per the control lines specified by the concerned government departments (such as the Public Works and Housing Department, Panchayat, National Highway Authority of India (N.H.A.I.), Railways, Irrigation, and Archaeology Departments) | |||
| 04 | Regarding the distance of the industrial unit from forest areas or seashore, the minimum distance must be maintained according to the category of the adjacent area (such as wildlife sanctuaries, national parks, protected forests, eco-sensitive zones, CRZ, etc.), as per the notifications issued from time to time by the government. | |||
The following details must be considered while applying the site selection criteria:
- Residential Area means an area where a cluster of fifteen (15) or more permanent houses is located.(site selection criteria)
- In cases where the industrial unit is being expanded or sold, if there is a change in the category, the site selection criteria will apply as per the new category.(site selection criteria)
- In cases where orders from the Honorable Supreme Court, Honorable NGT, or orders from the higher courts, or area-specific policies (Area-Specific Policy), industry-specific policies (Industry-Specific Policy), and government notifications are applicable, the provisions of such orders must be followed for site selection criteria.(site selection criteria)
- For industrial units located in the GIDC area, the site selection criteria will not apply; instead, the policy implemented by GIDC will have to be followed.(site selection criteria)
- All industrial units located in private estates without environmental clearance will be subject to site selection criteria.(site selection criteria)
- For service sector units under local self-governing bodies, such as hotels, automobile service stations, healthcare units, railway workshops/stations, all types of laboratories, gold hallmarking units, etc., the rules of the local self-governing bodies will apply for site selection criteria.(site selection criteria)
- In cases not covered under this circular regarding site selection criteria, they will be referred to the Board’s Site Selection Criteria Committee. (site selection criteria)
